|
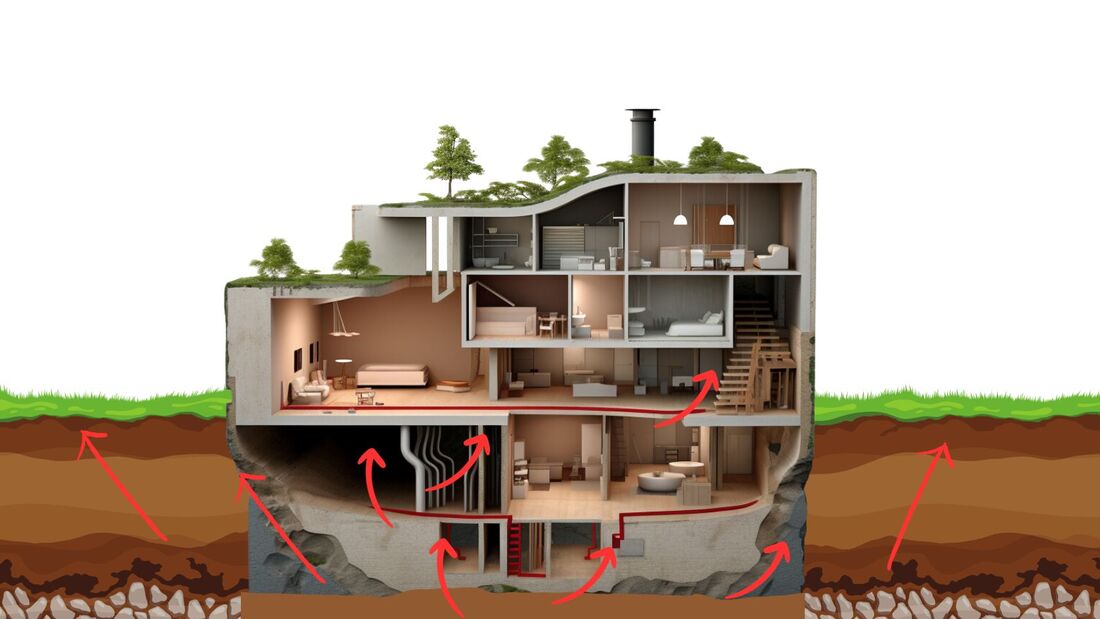
Radon is a silent, invisible threat that could be lurking in your home right now. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into what radon is, why it's dangerous, and, most importantly, how to reduce its associated risks. Radon may not be a household name, but it's a matter of life and death, and understanding how to deal with it can protect you and your loved ones. Read on to learn more. What Is Radon?Radon is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the environment. It is a byproduct of the decay of uranium in soil and rocks. When radon is released from the ground, it can seep into homes and buildings, posing serious health risks to occupants. Why Is Radon Dangerous? Radon is a known carcinogen, meaning it can cause cancer. When radon gas is inhaled, it can damage the cells lining the lungs, leading to lung cancer. It is the second leading cause of lung cancer, responsible for thousands of deaths each year. Unlike other environmental toxins, Radon cannot be seen or smelled, making it a particularly insidious threat. The Importance of Radon Reduction Reducing radon levels in your home is crucial for your family's health and safety. The longer you are exposed to elevated radon levels, the higher your risk of developing lung cancer. Fortunately, there are effective methods to reduce radon concentrations, making your home safer. Understanding RadonTo effectively combat radon, it's essential to understand its sources, how it enters homes, and how it's measured. Radon in Soil Radon is primarily generated in the soil beneath homes. It forms when uranium naturally decays, releasing radioactive particles. These particles mix with the air, creating radon gas that can migrate upward through the soil and into your home. Radon in Water In some areas, radon can also be present in groundwater. When you use water that contains radon for activities like showering or cooking, the gas can be released into the air, contributing to indoor radon levels. How Radon Enters Homes Radon enters homes through cracks and openings in the foundation and walls. It can seep through gaps around pipes, sump pumps, and drains. Understanding these entry points is crucial for effective mitigation. Radon Levels and Measurement Measuring radon levels is the first step in determining if your home is at risk. Radon levels are typically measured in picocuries per liter (pCi/L). The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends action if radon levels exceed 4 pCi/L. Various methods, including long-term and short-term tests, are available to assess radon levels in your home. Health Risks Associated with RadonLung Cancer Lung cancer is the most significant health risk associated with radon exposure. Prolonged exposure to elevated radon levels can increase the risk of lung cancer, especially among smokers. Radon-induced lung cancer is preventable through radon reduction measures. Other Health Concerns Apart from lung cancer, research is ongoing into other potential health risks associated with radon exposure. These include respiratory issues, especially in children, and the possibility of other cancers. While the evidence is not as clear-cut as with lung cancer, it underscores the importance of minimizing radon exposure. Who Is at Risk? Everyone is at some risk of radon exposure, but certain factors can increase your risk:
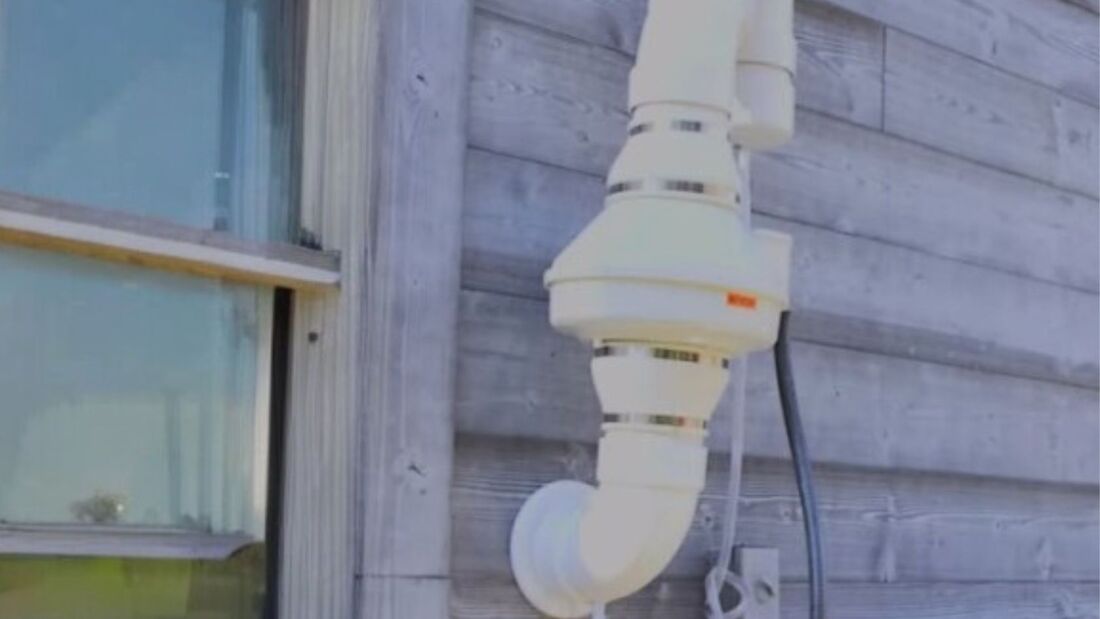
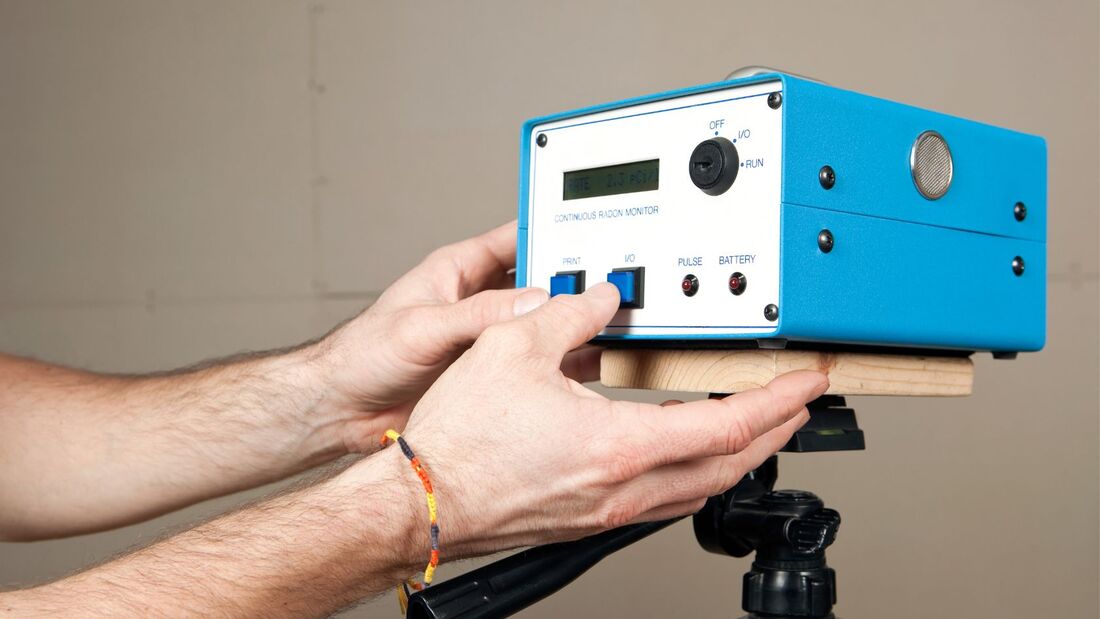
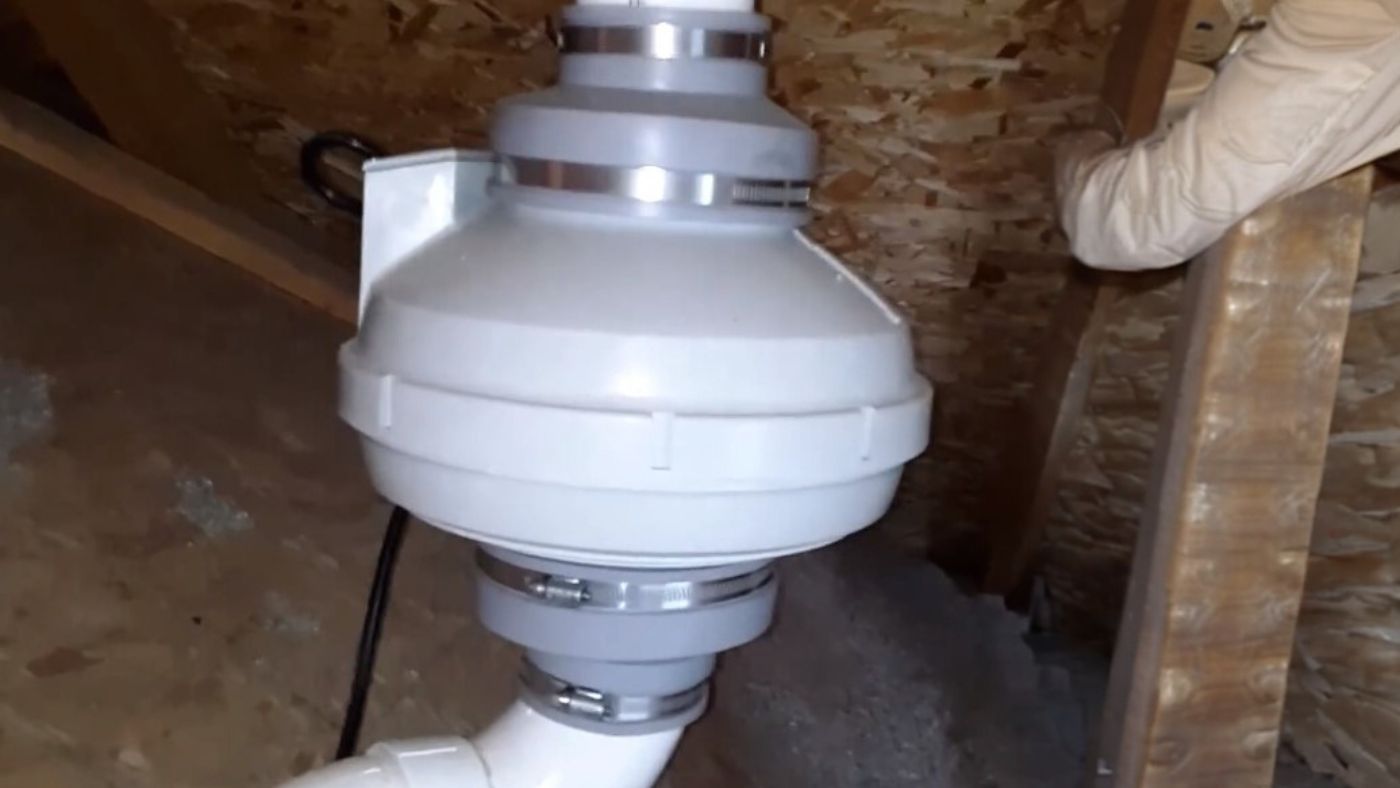
Understanding your risk factors can help you take appropriate action. How To Test Your HomeTesting your home for radon is the first step toward ensuring a safe living environment for you and your family. Radon Testing Short-Term Vs. Long-Term Testing Radon testing can be conducted using short-term or long-term methods. Short-term tests typically last two to seven days and provide a quick snapshot of radon levels. Long-term tests, however, measure radon levels for over 90 days, providing a more accurate picture of year-round exposure. DIY Testing Kits Do-it-yourself radon testing kits are readily available and cost-effective. These kits come with instructions on how to set up and use them. They are a convenient way to check your home's radon levels, but following the instructions carefully for accurate results is essential. When and How Often to Test Radon levels can vary throughout the year and may change over time. The EPA recommends testing your home every two years, especially if you've never tested it before. Additional testing is also advised if you've made structural changes to your home or have previously mitigated radon. Interpreting Radon Test Results When you receive the results of your radon test, it's essential to take action accordingly. Your home is considered safe if the test reveals radon levels below 4 pCi/L. However, if levels exceed this threshold, it's crucial to take steps to reduce radon concentrations. Radon Reduction MethodsRadon Mitigation Systems Active Soil Depressurization Active Soil Depressurization (ASD) is the most common and effective radon mitigation method. It involves installing a system that draws radon gas from beneath the foundation and vents it safely above the roofline. This creates a negative pressure zone beneath the home, preventing radon from entering. Passive Radon Systems Passive radon systems rely on natural ventilation and pressure differentials to reduce radon levels. While they are less effective than ASD systems, they can be a viable option in some cases. Sealing Cracks and Openings To complement radon mitigation systems, it's essential to seal cracks and openings in the foundation and walls. This prevents radon from finding new entry points into your home. Improving Ventilation Enhancing ventilation in your home can help reduce radon levels. Increasing airflow through exhaust fans and fresh air intakes can dilute radon concentrations. READ ABOUT : What is the lifespan of a radon mitigation system? Hiring a Radon ProfessionalQualifications to Look For When considering hiring a radon mitigation professional, it's crucial to ensure they are qualified and experienced. Look for the following qualifications:
Getting Multiple Quotes It's a good practice to obtain quotes from multiple radon professionals. This lets you compare services and pricing to ensure you get the best value for your radon mitigation project. Questions to Ask a Radon Contractor Before hiring a radon contractor, ask them the following questions:
CALL US: Radon Columbus Mitigation Expert ( 614-412-0949 ) Radon Awareness and AdvocacyPromoting Radon Awareness Radon awareness is critical in ensuring that more people take action to protect their homes and families. You can promote radon awareness by sharing information with friends, family, and your community. Encouraging Testing and Reduction Encourage others to test their homes for radon and take action if levels are elevated. You can catalyze change in your community by advocating for radon testing and mitigation. Government Initiatives Learn about government initiatives aimed at addressing radon-related issues. Some regions may offer financial incentives or support for radon testing and mitigation. ConclusionIn conclusion, radon is a hidden danger that can have devastating health consequences. However, by understanding the risks, testing your home, and taking appropriate mitigation measures, you can significantly reduce the threat of radon exposure. A safer, healthier home is within reach, starting with taking action today. Additional ResourcesRadon Organizations and Websites
For more information on radon and radon mitigation, you can visit the following organizations and websites:
0 Comments
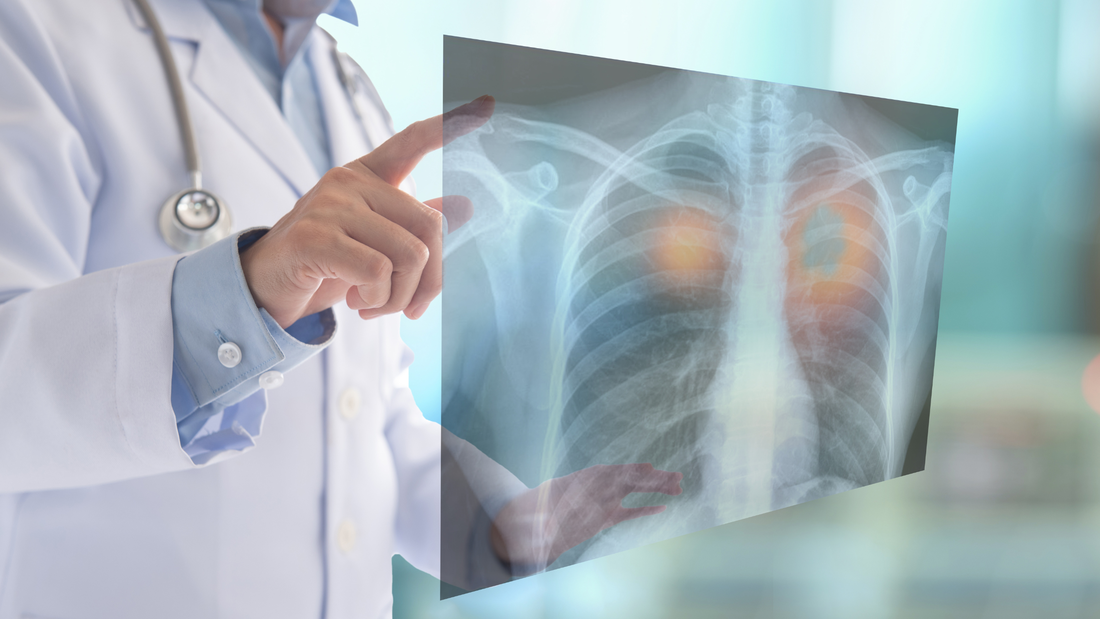
Radon, a colorless and odorless radioactive gas, poses a serious health risk when accumulating in enclosed spaces. Among the various health hazards associated with radon exposure, one of the most concerning is its potential to cause lung cancer. So, does radon cause lung cancer? In this article, we will delve into the relationship between radon and lung cancer, exploring how radon causes cancer, the types of cancer it can induce, and the number of individuals affected by this harmful gas. Additionally, we will share a compelling story of a lung cancer patient in Columbus, Ohio, whose experience has fueled radon detection and prevention advocacy. How Does Radon Cause Cancer?Radon gas, classified as a human carcinogen by reputable organizations such as the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the World Health Organization (WHO), can lead to cancer through inhalation. As radon undergoes decay, it releases minuscule radioactive particles called radon progeny. When inhaled, these particles can become lodged in the lungs and emit radiation. The emitted radiation can damage the DNA within lung cells, triggering mutations that can eventually progress into cancerous growths. What Kind of Cancer Does Radon Cause?The primary cancer associated with radon exposure is lung cancer. The EPA states that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. Approximately 21,000 lung cancer radon deaths in the United States annually are attributed to radon exposure. It is crucial to note that even individuals who have never smoked can develop lung cancer due to radon exposure. The risk of developing lung cancer due to radon exposure is influenced by factors such as the level of radon, the duration of exposure, and an individual's smoking history. How Many People Develop Lung Cancer Because of Exposure to Radon?Radon's impact on lung cancer is substantial, with approximately one in 15 homes in the United States having radon levels exceeding the EPA's recommended action level of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L). Recognizing the gravity of the situation, the Surgeon General has warned about radon lung cancer risk as a significant public health concern and advises that all homes undergo radon testing. Despite these recommendations, many individuals remain unaware of the dangers of radon and the necessity of testing their living environments. Lung Cancer Patient in Columbus, Ohio Advocates for Detection of RadonAnnie Cacciato, a non-smoker in Columbus, Ohio, had never anticipated being diagnosed with lung cancer. Following a fall that left her with bumps and bruises, she underwent a series of medical tests, only to receive a shocking stage four non-small cell lung cancer diagnosis. Determined to comprehend the possible causes of her illness, Annie conducted extensive research. She uncovered alarming information about radon levels in her former high school and workplace, which had significantly elevated radon levels, posing a risk for lung cancer. Motivated by her personal experience, Annie and her husband, John, embarked on a mission to raise awareness about radon exposure and its link to lung cancer. They became strong advocates for radon testing and implementing prevention measures in schools, workplaces, and residential settings. Their efforts gained traction, resulting in the Ohio House passing a bill in Annie's name that designates January as Radon Awareness Month within the state. Annie's story is a powerful reminder that radon can impact individuals from all walks of life, irrespective of their smoking history. Read more about Lung cancer patient advocates for the detection of radon. ConclusionRadon, a silent and invisible threat, has been unequivocally linked to the development of lung cancer. The radioactive particles released by radon can harm the DNA of lung cells, eventually leading to the formation of cancerous cells. Recognizing that radon-induced lung cancer can affect smokers and non-smokers alike is crucial, underscoring the significance of radon testing and mitigation measures for all individuals. Annie Cacciato's journey is a testament to the urgent need for radon awareness, detection, and prevention efforts to safeguard public health. FAQsWhat is radon?Radon is an odorless, tasteless, and colorless radioactive gas that occurs naturally in minerals, soil, and water due to the decay of uranium. How does radon enter homes?Radon can enter residences through foundation cracks, wall or floor openings, and water sources such as wells. It can accumulate in confined spaces, increasing the exposure risk. Can radon cause lung cancer?Radon is a known carcinogen associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. Long-term radon exposure can damage lung tissue and promote the growth of malignant cells. Are smokers more at risk of radon-induced lung cancer?Yes, smokers are at a higher risk of developing lung cancer from radon exposure. When combined with smoking, the risk of lung cancer increases significantly. However, even non-smokers can develop lung cancer due to radon exposure. How prevalent is radon-induced lung cancer?Radon exposure accounts for approximately 15% of all lung cancer cases worldwide. In the United States, it is the second leading cause of lung cancer, resulting in thousands of deaths yearly. How can I test my home for radon?Radon testing kits are available for home use. These kits can be placed in various home areas, such as basements or living spaces, to measure radon levels. Alternatively, you can hire a professional radon testing service to assess your home. What is considered a safe level of radon?There is no known amount of radon that is safe. But the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States suggests taking steps to lower radon levels if they are higher than four pCi/L. How can I mitigate radon in my home?Radon mitigation techniques include:
Is there a way to prevent radon-induced lung cancer?While eliminating radon is impossible, you can take steps to reduce your exposure. Testing your home for radon and implementing mitigation measures, if necessary, can help lower the risk of radon-induced lung cancer. Are there any regulations or guidelines regarding radon?Many countries, including the United States, have established guidelines and regulations regarding radon. These guidelines frequently advocate for radon testing and mitigation techniques to protect people from the health concerns connected with radon exposure.
Radon is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless radioactive gas that can seep into homes and pose serious health risks. To protect ourselves and our loved ones, installing a radon mitigation system is crucial. But have you ever wondered about the lifespan of such a system? How long can we rely on it to effectively reduce radon levels in our homes? Let's explore the lifespan of a radon mitigation system, shedding light on important factors that can impact its longevity and maintenance requirements. What Affects Radon Mitigation System Lifespan?Here are the key factors that determine the lifespan of a radon mitigation system: Quality of InstallationWhen it comes to a radon mitigation system's lifespan, proper installation is paramount. A system that certified radon mitigation experts professionally install is likely to have a longer lifespan than an improperly installed system. This is because a correctly installed system will more efficiently reduce radon levels and experience fewer issues over time. Type of SystemDifferent types of radon mitigation systems are available, such as active sub-slab suction, submembrane suction, and heat recovery ventilation. The lifespan of a radon mitigation system can vary depending on the type chosen. Active sub-slab suction systems, for example, are known for their durability and can last for 10 to 20 years with proper maintenance. On the other hand, other types of systems may have a shorter lifespan and require more frequent inspections and repairs. Maintenance and Regular InspectionsRegular maintenance and inspections are crucial to ensure the longevity of your radon mitigation system. You should look at your warning device regularly to ensure the system works correctly. Fans may last for five years or more (manufacturer warranties tend not to exceed five years) and may need to be repaired or replaced. Additionally, it is recommended to have a professional inspection every 1 to 2 years to check the system's performance, identify any potential issues, and perform necessary repairs or replacements. Environmental FactorsEnvironmental factors can also play a role in the lifespan of a radon mitigation system. The soil conditions, climate, and indoor air quality can impact the system's efficiency and longevity. Harsh weather conditions, high humidity levels, and other contaminants in the soil or air can affect the system's components and performance. Therefore, it's essential to consider these factors and take appropriate measures to protect and maintain your radon mitigation system. Upgrades and Technological AdvancementsAs with any technology, radon mitigation systems continue evolving and improving. Newer systems may incorporate advanced features and technologies that enhance performance and durability. If you have an older system, it's worth considering an upgrade to take advantage of the latest advancements in radon mitigation. Upgrading to a newer system may not only extend the lifespan of your system but also provide you with better radon reduction efficiency and energy savings. Local Regulations and GuidelinesAwareness of the local regulations and guidelines regarding radon mitigation systems is essential. These regulations can vary from region to region and may include system installation, maintenance, and testing requirements. Adhering to these regulations and guidelines can help ensure your system is installed correctly and maintained, ultimately contributing to its longevity and effectiveness. Final ThoughtsThe lifespan of a radon mitigation system can depend on various factors, including the quality of installation, type of system, maintenance and regular inspections, environmental factors, upgrades, technological advancements, and adherence to local regulations. By considering these factors and taking proactive measures to maintain and care for your system, you can maximize its lifespan and continue to protect your home and loved ones from the dangers of radon. Remember to consult with certified radon mitigation professionals for guidance on system installation, maintenance, and any necessary upgrades. Stay informed, stay safe, and enjoy peace of mind knowing you have a reliable radon mitigation system. FAQsIs professional installation necessary for a radon mitigation system?Yes, it is highly recommended to have a radon mitigation system installed by certified professionals. Proper installation is crucial for the system's effectiveness and longevity. Certified experts have the knowledge and expertise to assess your home's radon levels, determine the appropriate system type, and ensure proper installation according to industry standards. Do different types of radon mitigation systems have different lifespans?Yes, different types of radon mitigation systems can have varying lifespans. For example, active sub-slab suction systems are known for their durability and can last 10 to 20 years or more with proper maintenance. Other systems may have shorter lifespans and require more frequent inspections and repairs. How often should I maintain and inspect my radon mitigation system?Regular maintenance and inspections are essential for the longevity and effectiveness of your radon mitigation system. Regularly inspecting your system, including the warning device, is recommended. Fans, an integral part of the system, may need to be repaired or replaced after around five years of use. Additionally, every 1 to 2 years, professional inspections are advised to assess the system's performance and promptly address any issues. Can environmental factors affect the lifespan of a radon mitigation system?Yes, environmental factors can play a role in the lifespan of a radon mitigation system. Harsh weather conditions, high humidity levels, and other contaminants in the soil or air can potentially impact the system's components and performance. Considering these factors and taking appropriate measures to protect and maintain your system is essential. Are there any upgrades or advancements in radon mitigation systems?Yes, radon mitigation systems continue to evolve and improve over time. Upgrading newer systems incorporating advanced features and technologies can enhance the system's performance, durability, and radon reduction efficiency. It is worth considering an upgrade if you have an older system to take advantage of these advancements. Yes, radon mitigation systems continue to evolve and improve over time. Upgrading newer systems incorporating advanced features and technologies can enhance the system's performance, durability, and radon reduction efficiency. It is worth considering an upgrade if you have an older system to take advantage of these advancements.
|
AuthorRadon Columbus Mitigation Expert Archives
September 2023
Categories |
|
SERVING COLUMBUS OHIO & SURROUNDING AREAS
|
BUSINESS NAP
Columbus Ohio Radon Mitigation 35 E 8th Ave #303 Columbus, OH 43201 BUSINESS HOURS Mon-Sunday: 7AM-7PM OUR SERVICES Radon Mitigation Radon Testing Radon System Installation ABOUT US CONTACT |
CLICK TO CALL!
614-412-0949 SOCIAL MEDIA
|